
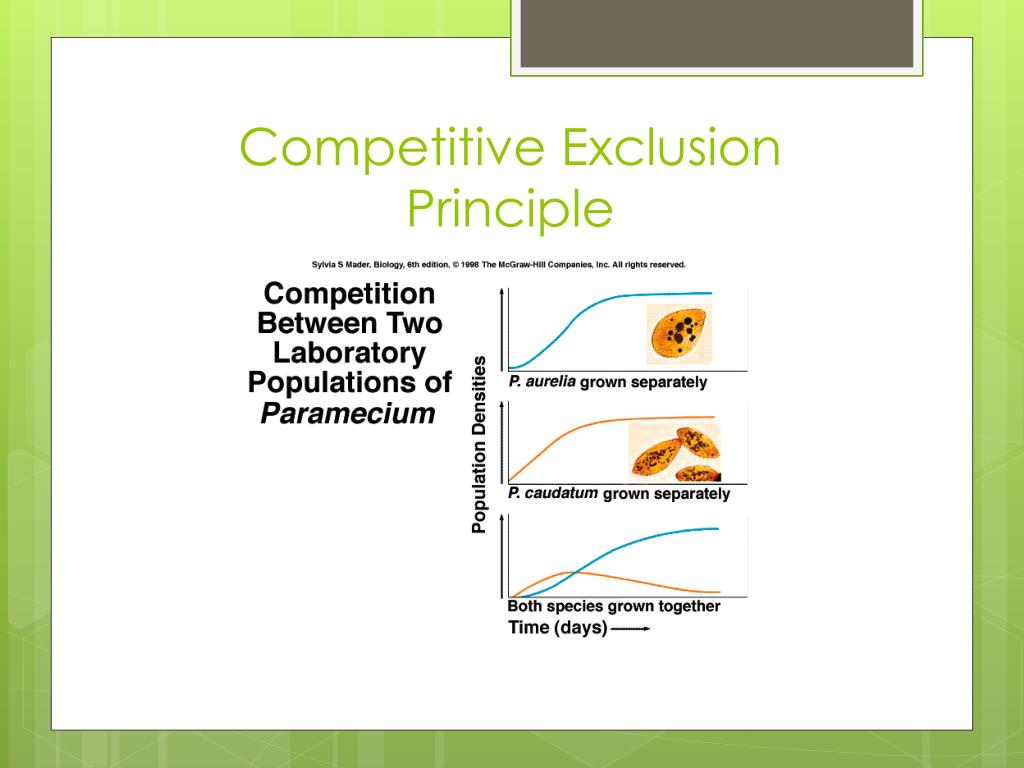
This is the basis of Niels Bohr's explanation of the periodic table. Using the fact that a system will try to occupy the state of lowest possible energy, the electron configuration of atoms may be understood by simply filling the single-particle energy levels according to the Pauli principle. See Angular momentum, Quantum numbers, Spin (quantum mechanics) It plays a central role in the understanding of many diverse phenomena, including the periodic table of the elements and their chemical activities, the electron contribution to the specific heat of metals, the shell structure in the atomic nucleus analogous to that of electrons in atoms, and certain symmetries in the scattering of identical particles. In addition to electrons, all known particles having half-integer intrinsic angular momentum, or spin, obey the exclusion principle. 1292 - 1297 DOI: 10.1126/science.131.3409. In ecology, the competitive exclusion principle, sometimes referred to as Gauses law, is a proposition named for Georgy Gause that two species competing. This principle, often called the Pauli principle, was first formulated by Wolfgang Pauli in 1925 and, for time-independent quantum states, it means that no two electrons may be described by state functions which are characterized by exactly the same quantum numbers. Article The Competitive Exclusion Principle: Garrett Hardin Authors Info & Affiliations Science Vol 131, Issue 3409 pp. The Principle of Competitive Exclusion, first articulated by Gause in 1934, states that two species or populations cannot inhabit the same niche: one will consistently out-compete the other. No two electrons may simultaneously occupy the same quantum state. Another way of expressing this idea is that 'complete competitors' cannot coexist. This is the definition of the competitive exclusion principle.The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia™ Copyright © 2022, Columbia University Press. The competitive exclusion principle states that two species that occupy the same biological niche cannot coexist. Two species in an area cannot have the same Mitch right. Well, the kid, the competitive exclusion principle says that two species in an area make sure you got that right. It's all the resource is that it needs uniquely to itself. at intermediate levels of disturbance, diversity is maximized because species that thrive at both early and late successional stages can coexist, III. at low levels of ecological disturbance species richness decreases as competitive exclusion increases, II. It's basically a specific set of factors that are specific to an individual. Graph shows principles of intermediate disturbance hypothesis: I. This ideal niche that would exist in the absence of competition. You may have heard this term of four Bonanza. This direct form of competition for an ecological niche is called interspecific competition.
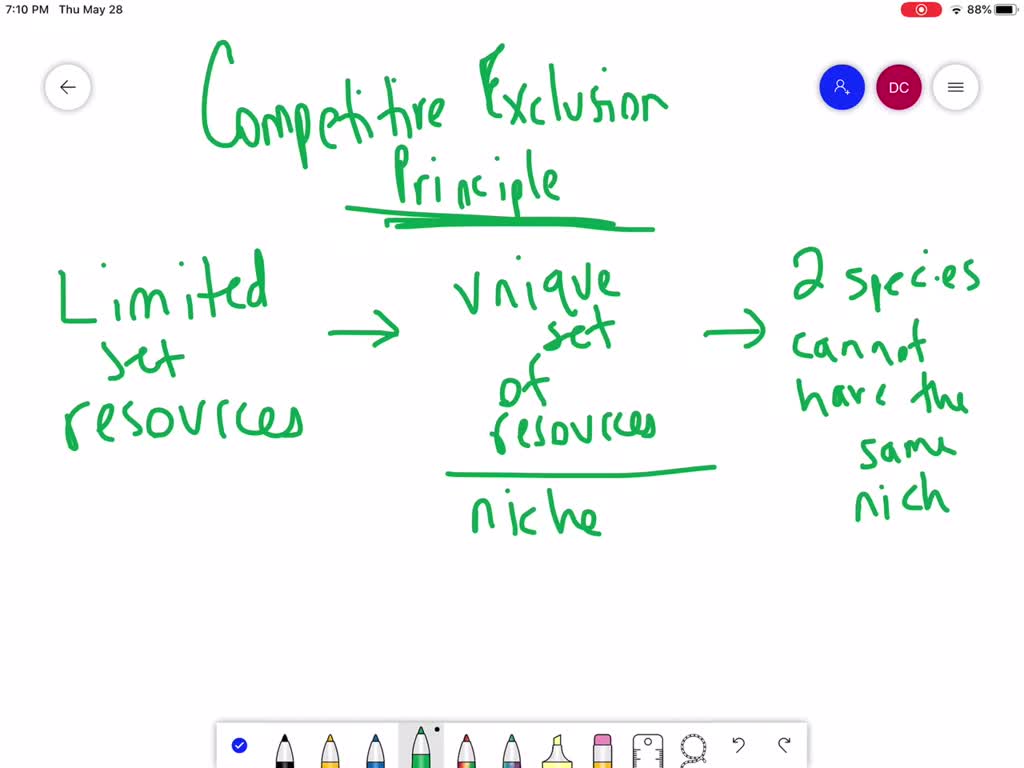
Um this unique set of resource is needed by, um an organism is called a niche. A generalization of the competitive exclusion principle is that coexistence of n species requires n limiting factors, and n distinct feedback effects via the environment. It needs a certain type of environment toe livin to produce offspring in to get food from to get water from whatever, whatever it needs.

Whatever you have requires, a unique set of resource is to survive. Each organism inside of, ah, environment inside of an ecosystem habitat. In an environment, you have a limited set of resource Is food, water, um, shelter so forth. So I'm just going to use a little train of thoughts here to get to the definition of this principle. Competitive exclusion: One species will use the resources more efficiently and drive the other species to local extinction Resource partitioning: Two. According to this principle, if there are two. In this question, we are going to look at a term called the competitive exclusion Principle. The definition of the competitive exclusion principle says that the niche of a species cannot be the exact same as another species in the ecosystem. The principle of competitive exclusion, developed in relation to microorganisms, states that if two species occupy the same ecological niche, defined as the. competitive exclusion principle ( exclusion principle, Gause principle) The principle that two or more resource-limited species, having identical patterns of resource use, cannot coexist in a stable environment: one species will be better adapted and will out-compete or otherwise eliminate the others.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
